Class-12 Ch-8 Electromagnetic Waves

About Course
Electromagnetic Waves class 12 notes (Free)
Ch-7 Electromagnetic Waves
Topic Covered
–Latest CBSE syllabus 2023-2024
-Introduction, Maxwell Displacement Current
-Maxwell Continuity Equations
-Properties of Electromagnetic Waves
-Propagation of Waves
-Electromagnetic Spectrum
-Frequency and Wavelength of E.M Waves
-All important CBSE Numerical
CBSE Chapter 8 Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Notes
How Are Electromagnetic Waves Formed?
- Typically, a charged particle generates an electric field. This electric field applies a forces on the other charged particle. Negative charges accelerate in the opposite direction from the direction of the field, whereas positive charges accelerate in the direction of the field.
- There is a moving charged particle that creates the magnetic field. This magnetic field applies force to other moving particles. These charges are subject to a force that is constantly perpendicular to the direction of their velocity; as a result, only the direction of velocity is altered, not the speed.
- Therefore, a charged particle that is speeding produces the electromagnetic field. All that exists between electric and magnetic forces flowing across free space at the speed of light (c) is electromagnetic waves. When the charged particles oscillates about an equilibrium location, it is said to be accelerating. An electromagnetic wave with frequency f is produced when a charged particle oscillates at a frequency of f. λ = c/f gives the wavelength λ of this wave. Electromagnetic waves transfer energy through space.
IMPORTANT for Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 notes.
- Displacement Current: It is by the time-varying electric field –
Displacement current acts as a sources of magnetic fields in exactly the same way as electronic current flow in conducting wires. - Maxwell’s equations:
- Gauss law of electrostatics-
- Gauss law of magnetism-
- Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction-
- Modified form of Ampere’s circuital law-
IMPORTANT for Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 notes.
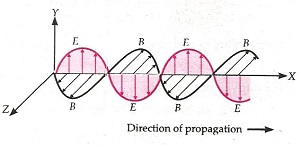
- Electromagnetic Waves: These waves propagates through space as coupled magnetic and electric fields, oscillating perpendicular to each other and in the direction of the propagation of wave.

- Electromagnetic waves are produced only by charges that are accelerating, since acceleration is absolute, and not a relative phenomena.
- An electric charge oscillating harmonically with frequency , produces electromagnetic waves of the same frequency .
- The first electromagnetic waves were created and observed in a laboratory by Hertz in 1887. They had a wavelength of a few metres. As a result, he confirmed a fundamental Maxwellian prediction.
- Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature.
- They do not require any type of medium for their propagation.
- Oscillation of Electric and Magnetic Fields: These oscillate sinusoidal in space and time in an electromagnetic wave. The oscillating magnetic and electric fields, E and B are perpendicular to each other and in the direction of propagation of electromagnetic wave.
- For a wave of frequency , wavelength , propagating along z-direction
IMPORTANT for Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 notes.
- Relation between and : The speed c of electromagnetic wave in vacuum is related to and (the free space permeability and permittivity constants) as
- The value of c equals the speed of light obtained from optical measurements.
- Light is an electromagnetic wave.
- Electromagnetic waves travelled in space with the same velocity c in free space.
- Speed of Light: The speed of light, or of electromagnetic waves in a material medium is
Where is the permeability of the medium and its permittivity.
- Electromagnetic waves carry energy as they travel in space and this energy is shared equally by the magnetic and electric fields.
- Energy Per Unit Volume: there is a region of space in which there exist electric and magnetic fields , there exists Energy Density (Energy per unit volume) associated with these fields is,
where we are assuming that the concerned space consists of vacuum only. - Electromagnetic waves transport momentum as well. When these waves strike a surface, a pressure is exerted on the surface.
- If total energy transferred to a surface in time t is U, total momentum delivered to this surface is p = U/c.
- Electromagnetic Spectrum: The electromagnetic spectrum is the orderly distribution of electromagnetic waves according to their wavelength or frequency into various groups with significantly different qualities.
- The process of producing and detecting these waves is more important to the classification.
- Different Regions of Spectrum: Different regions are known by different names; -rays, X-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible rays, infrared rays, microwaves and radio waves in order of increasing wavelength from or to IMPORTANT for Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 notes.
In Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 physics Notes
(a) Radio Waves:
- These are produced by accelerated motion of charge particles.
- These are used in television and radio communication systems.
- These are generally in the frequency range from 500 kHz to about 1000 MHz or wavelength range 600 m to 0.1 m.
(b) Microwaves:
- These are short wavelength radio waves with frequency range 109 Hz to 1012 Hz or wavelength range 0.3 m to 10-3 m.
- They are appropriate for radar systems used in aviation navigation because of their short wavelengths.
- Microwave ovens use them for cooking.
(c) Infrared Waves:
- Frequency range or wavelength range
- Both hot bodies and molecules produce them.
- They are located in the visible spectrum’s long wavelength or low frequency range.
(d) Visible Light:
- The spectrum frequency runs from about 4 x to about 7 x or wavelength range .
- Our eyes are sensitive to this range of wavelengths.
(e) Ultraviolet light:
- It covers frequency range from or wavelengths range from .
- The sun is an important source of UV rays.
(f) X-rays:
- It covers frequency range from or wavelengths range from .
- It is used in medical diagnosis.
(g) Gamma Rays:
- These lie in the upper frequency range of the spectrum, and have wavelengths in the range to .
- It is used in manufacture of polyethylene from ethylene.
Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature. The highest point of the wave is known as the crest while the lowest point is known as a trough. IMPORTANT for Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 notes.
Course Content
Class-12 Physics Ch-8 Electromagnetic Waves
Lecture-1 (Introduction, Maxwell Displacement Current, Maxwell Equation, Properties of EM Waves)
00:00Lecture-2 (Electromagnetic Spectrum, Frequency, Wavelength and Uses of E.M Waves)
00:00
Student Ratings & Reviews

No Review Yet