Table of Contents
ToggleNCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity)
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Intext Questions
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity)
Page Number: 172
Question 1
What does an electric circuit mean ?
Answer:

Question 2
Define the unit of current.
Answer:

Question 3
Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
Answer:

NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity)
Page Number: 174
Question 1
Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor.
Answer:
Question 2
What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is 1 V?
Answer:

Question 3
How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V battery ?
Answer:

NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity)
Page Number: 181
Question 1
On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend ?
Answer:

Question 2
Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source ? Why ?
Answer:

Question 3
Let the resistance of an electrical component remains constant while the potential difference across the two ends of the component decreases to half of its former value. What change will occur in the current through it ?
Answer:

Question 4
Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons are made of an-alloy rather than a pure metal ?
Answer:

Question 5
Use the data in Table 12.2 (in NCERT Book on Page No. 179) to answer the following :
(i) Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor ?
(ii) Which material is the best conductor ?
Answer:

NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity)
Page Number: 185
Question 1
Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of a battery of three cells of 2 V each, a 5Ω resistor, an 8 Ω resistor, and a 12 Ω resistor, and a plug key, all connected in series.
Answer:

Question 2
Redraw the circuit of Questions 1, putting in an ammeter to measure the current through the resistors and a voltmeter to measure the potential difference across the 12 Ω resistor. What would be the readings in the ammeter and the voltmeter ?
Answer:

NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity)
Page Number: 188
Question 1
Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel:
(a) 1 Ω and 106 Ω
(b) 1 Ω and 103 Ω, and 106 Ω
Answer:

Question 2
An electric lamp of 100 Ω, a toaster of resistance 50 Ω, and a water filter of resistance 500 Ω are connected in parallel to a 220 V source. What is the resistance of an electric iron connected to the same source that takes as much current as all three appliances, and what is the current through it ?
Answer:

Question 3
What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series ?
Answer:

Question 4
How can three resistors of resistances 2Ω, 3 Ω, and 6Ω be connected to give a total resistance of (i) 4 Ω, (ii) 1 Ω ?
Answer:

Question 5
What is (i) the highest, (ii) the lowest total resistance that can be secured by combinations of four coils of resistance 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω, 24 Ω?
Answer:

NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity)
Page Number: 190
Question 1
Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does ?
Answer:

Question 2
Compute the heat generated while transferring 96000 coulomb of charge in one hour through a potential difference of 50 V.
Answer:

Question 3
An electric iron of resistance 20Ω takes a current of 5 A. Calculate the heat developed in 30 s.
Answer:

NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity)
Page Number: 192
Question 1
What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current ?
Answer:

Question 2
An electric motor takes 5 A from a 220 V line. Determine the power of the motor and the energy consumed in 2 h.
Answer:

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Exercise Questions (Textbook Chapter End Questions)
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity)
Question 1
A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into five equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this combination is R’, then the ratio R/R’ is :
(a) 125
(b) 15
(c) 5
(d) 25
Answer:

Question 2
Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit?
(a) I2R
(b) IR2
(c) VI
(d) v22
Answer:

Question 3
An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V, the power consumed will be :
(a) 100 W
(b) 75 W
(c) 50 W
(d) 25 W
Answer:

Question 4
Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in series and then parallel in a circuit across the same potential difference. The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations would be :
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 2 : 1
(c) 1 : 4
(d) 4 : 1
Answer:
Question 5
How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points ?
Answer:
Question 6
A copper wire has diameter 0.5 mm and resistivity of 1.6 x 10-8 Ω m. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance 10 Ω ? How much does the resistance change if the diameter is doubled ?
Answer:

Question 7
The values of current I flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference V across the resistor are given below :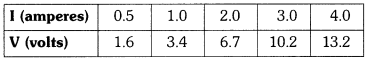 Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of the resistor.
Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of the resistor.
Answer:

Question 8
When a 12 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current of 2.5 mA in the circuit. Find the value of the resistance of the resistor.
Answer:

Question 9
A battery of 9 V is connected in series with resistors of 0.2 Ω, 0.3 Ω, 0.4 Ω, 0.5 Ω and 12 Ω, respectively. How much current would flow through the 12 Ω resistor?
Answer:

Question 10
How many 176 Ω resistors (in parallel) are required to carry 5 A on a 220 V line?
Answer:

Question 11
Show how you would connect three resistors, each of resistance 6 Ω, so that the combination has a resistance of (i) 9 Ω, (ii) 4Ω
Answer:


Question 12
Several electric bulbs designed to be used on a 220 V electric supply line, are rated 10 W. How many lamps can be connected in parallel with each other across the two wires of 220 V line if the maximum allowable current is 5 A ?
Answer:

Question 13
A hot plate of an electric oven connected to a 220 V line has two resistance coils A and B, each of 24 Ω resistance, which may be used separately, in series, or in parallel. What are the currents in the three cases ?
Answer:

Question 14
Compare the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits
(i) a 6 V battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors, and
(ii) a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
Answer:

Question 15
Two lamps, one rated 100 W at 220 V, and the other 60 W at 220 V, are connected in parallel to electric mains supply. What current is drawn from the line if the supply voltage is 220 V ?
Answer:

Question 16
Which uses more energy, a 250 W TV set in 1 hr, or a 1200 W toaster in 10 minutes ?
Answer:

Question 17
An electric heater of resistance 8 Ω draws 15 A from the service mains 2 hours. Calculate the rate at which heat is developed in the heater.
Answer:

Question 17
Explain the following:
(a) Why is tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps ?
(b) Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal ?
(c) Why is the series arrangement not used for domestic circuits ?
(d) How does the resistance of a wire vary with its area of cross-section ?
(e) Why are copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity transmission?
Answer:



Light Reflection and Refraction in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity): You candidates may obtain class 10 NCERT solutions for electricity in this page. Practicing the light chapter of the Class 10 NCERT answers will assist candidates in developing a solid understanding of Physics. Understanding class 10 questions and answers related to light reflection and refraction will also help students achieve a respectable grade on their class 10 board exams.
This post contains class 10 numerical problems related to light reflection and refraction in addition to the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity). Examining them will provide candidates a clear understanding of how to approach the difficulties, which will enable you to find the most effective solution. Why then wait? Discover everything there is to know about light reflection and refraction in class 10 by reading on for key questions and answers.
The organisation of NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity) presents a clear overview of scientific subjects that are relevant to everyday life. Students have been taught basic science with no clear distinctions between subjects like biology, chemistry, and physics. All of the country’s schools acknowledge and promote NCERT. Here are some explanations for why you should trust NCERT Solutions:
Students are forced to think creatively and apply the principles they have learnt in the chapter by the challenging questions that are put between the chapters.
You may get comprehensive answers to the chapter problems in NCERT Solutions, which will help you do well on the CBSE exams.
Students like using NCERT Solutions, particularly in the subjects of science and maths. This section contains the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity). The solutions to all of the problems in the textbook are clearly explained. Get the complete set of NCERT Solutions for Light Reflection and Refraction in Chapter 10 here for free!
One of the most significant chapters in Class 10 Science is NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity). The most recent marking scheme assigns a weightage of 7 marks to this chapter. Students will gain a thorough understanding of light phenomena including refraction and reflection in Class 10 Science’s NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity) Drawing ray diagrams, spherical mirrors, and image generation will all be covered.
Ever wonder why certain things are visible to us? Light is the answer to the query. Sunlight aids in our ability to see items during the day. An item reflects light when it hits it. When this reflected light reaches our eyes, it aids in our ability to see. Light is responsible for many amazing occurrences, like the birth of stars and rainbows, among many others. Let’s examine the phenomena of refraction and reflection utilising the straight-line propagation of light in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity). In this chapter, we will also attempt to comprehend how spherical mirrors reflect light by utilising the NCERT Solutions from Bhautik Study.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 (Electricity): Key Elements of the NCERT Solutions
offers thorough responses to every query posed in the chapter.
The material offered is accurate and suitable, and the language used is clear and understandable to all.
You can use these solutions for Olympiads, CBSE exams, and other competitive exams.
Students are given concise responses to aid in their understanding.